Go to Quantitative Methods
Topics
Table of Contents
Introduction
- What is
Fintechand how it is used in Investment Analysis? - A brief explanation of Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, and Machine Learning
- Applications of Big Data and Data Science to Investment Management
How Is Fintech Used in Quantitative Investment Analysis?
The term Fintech comes from combining Finance and Technology.
Fintech refers to technological innovation in the design and delivery of financial products and services.
Its earlier forms involved data processing and automation of routine tasks. It later advanced into decision-making applications based on complex machine learning logic.
The major drivers of fintech have been:
- Rapid growth in data
- Technological advances
We focus on quantitative analysis in the investment industry:
- Analysis of large datasets
- Analytical tools
Big Data
Big Data refers to vast amount of data generated by industry, governments, individuals, and electronic devices.
Characteristics of big data
- Volume: Amount of data that we are dealing with has grown exponentially.
- Velocity: Speed at which data are communicated.
- Batch processing → Real time data
- Variety: Structured → Unstructured data.
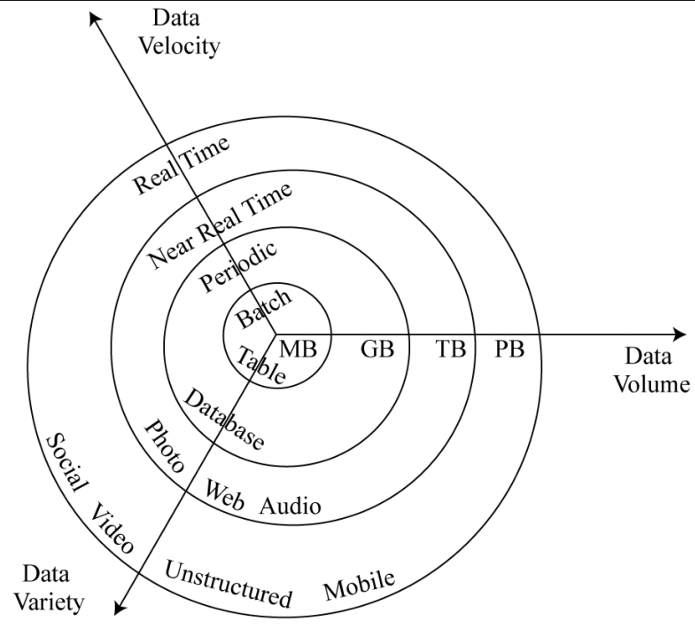
| Data | Volume Key | Bytes of Info |
|---|---|---|
| MB | MegaByte | 1 M |
| GB | GigaByte | 1 B |
| TB | TeraByte | 1 T |
| PB | PetaByte | 1 Q |
| In addition to these three V’s, a fourth V is becoming increasingly important, especially when using big data for drawing inferences or making predictions. |
- Veracity – Credibility and reliability of different data sources.
Big Data can be structured (can be organized in tables), semi-structured, or unstructured (cannot be represented in a tabular form).
Sources of Big Data
- Traditional data sources include annual reports, regulatory filings, trade price and volume, etc.
- Alternate data include many other sources and types of data.
| Individuals | Biz Process | Sensors |
|---|---|---|
| Social Media, Reviews | Transaction Data | Satellites |
| News | Corporate Data | Geolocation |
| Web Searches | IoT | |
| Personal Data | Other Sensors | |
| Big Data Challenges |
- The quality of data may be questionable.
- The data may have biases, outliers, etc.
- The volume of data collected may not be sufficient.
- Another concern is the appropriateness of data.
- Usually involves cleansing and organizing the data before we start analyzing it.
Advanced Analytical Tools: Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence
- Computers perform tasks that have traditionally required human intelligence.
AIexhibits cognitive and decision-making ability comparable or superior to that of human beings.Neural networksrefers to programming based on how the brain learns and processes information.
Chess playing computer programs, Digital assistants like Apple’s Siri, etc.
Machine Learning
Computer-based techniques that extract knowledge from large amounts of data by learning from known examples and then generating structure or predictions without relying on any help from a human.
In ML, the dataset is divided into three distinct subsets:
- Training dataset: Allows the algorithm to identify relationships between inputs and outputs based on historical patterns in the data.
- Validation dataset: Used to validate and model tune the relationships.
- Test dataset: Used to test the model’s ability to predict well on new data.
Broadly speaking there are three main approaches to machine learning:
- Supervised learning: Both inputs and outputs are labeled. After learning from labeled data, the trained algorithm is used to predict outcomes for new data sets.
- Unsupervised learning: Input and output variables are not labeled. The ML algorithm has to seek relationships on its own.
- Deep learning: Neural networks are used by the computers to perform multistage, non-linear data processing to identify patterns.
For ML to work well, good human judgment is required.
Human judgment is required for questions like:
- Which data to use
- How much data to use
- Which analytical techniques are relevant
- Clean and filter the data
Deep learning algorithms are used for image, pattern, and speech recognition.
Some challenges associated with machine learning are:
- Over-fitting the data: Sometimes an algorithm may try to be too precise. This leads to over-trained models and data mining bias.
- Mitigate this by having a good validation dataset.
- Black box: ML techniques can be opaque with predictions that are not very easy to explain.
Tackling Big Data with Data Science
Data science leverages advances in computer science, statistics, and other disciplines for the purpose of extracting information from Big Data.
Data Processing Methods
- Capture: How data is collected from various sources and transformed.
- Curation: Ensuring data quality and accuracy through data cleaning.
- Storage: How data will be recorded and accessed.
- Refers to the underlying databases design
- Whether the data is structured, unstructured, or both
- Need real time access to the data or not.
- Search: How we can find what we want from the vast amount of data.
- Transfer: How data will move from the source to the tools that are being used.
Data Visualization
How the data will ultimately be presented to the analyst/user.
Data Visualization
Graphs, Charts → Heat Maps, Tree Diagrams, and Tag Clouds
- Heat map of a city where routes with high traffic congestion are shown in red.
- A tag cloud works on textual data where words that appear more often are shown in larger font.

Text Analytics and Natural Language Processing
Text Analytics
Use of computer programs to derive meaning from large, unstructured text or voice-based data. Based on this, we can determine if the sentiment is very positive, positive, neutral, or negative.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Application of text analytics whereby computers analyze and interpret human language. Such processing is possible because of access to Big Data and processing power.
- Gauge the consumer sentiment about a new product by analyzing what is being said about the product.
- Used to gain insights in communications from policy makers who use a more formal tone.